- INTRODUCTION
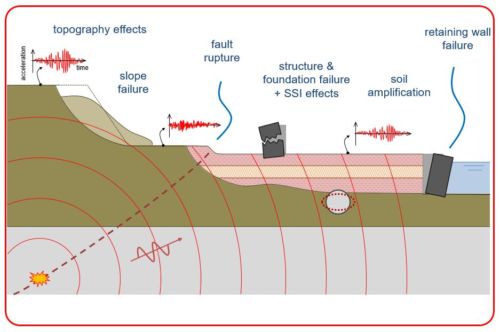
Definition of dynamic soil loading, types of dynamic soil loadings, special characteristics of dynamic soil loadings, methodology for analyzing and designing geotechnical systems under dynamic loading
- ELEMENTS OF THEORY OF VIBRATION
Time-dependent motion of soil element, mathematical description, non-periodic, periodic and harmonic motion. Fourier Analysis. The single degree of freedom system, natured frequency, damping, free and forced vibrations. Measurement of vibrations, resonance tests. Two degree of freedom systems, coupled vibrations
- WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOILS
The wave concept, wave propagation in homogeneous elastic half-space, longitudinal and shear body waves, surface waves (Rayleigh and Love), wave length, natural frequencies and normal modes of vibration of soil systems. Layered half-space, reflection and refraction of waves at soil interfaces, wave propagation in porous soil media, effect of water table.
- EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC SOIL PROPERTIES
Field methods (Direct wave propagation, wave reflection and refraction methods, surface wave methods-SASW, MASW , Cross-hole method). Laboratory methods (Resonant column method, cyclic triaxial, simple shear and torsional hollow cylinder test methods) Indirect methods (Hardin equation, correlations with NSPT, CPT and shear strength, τmax )
- DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR OF SOIL ELEMENT
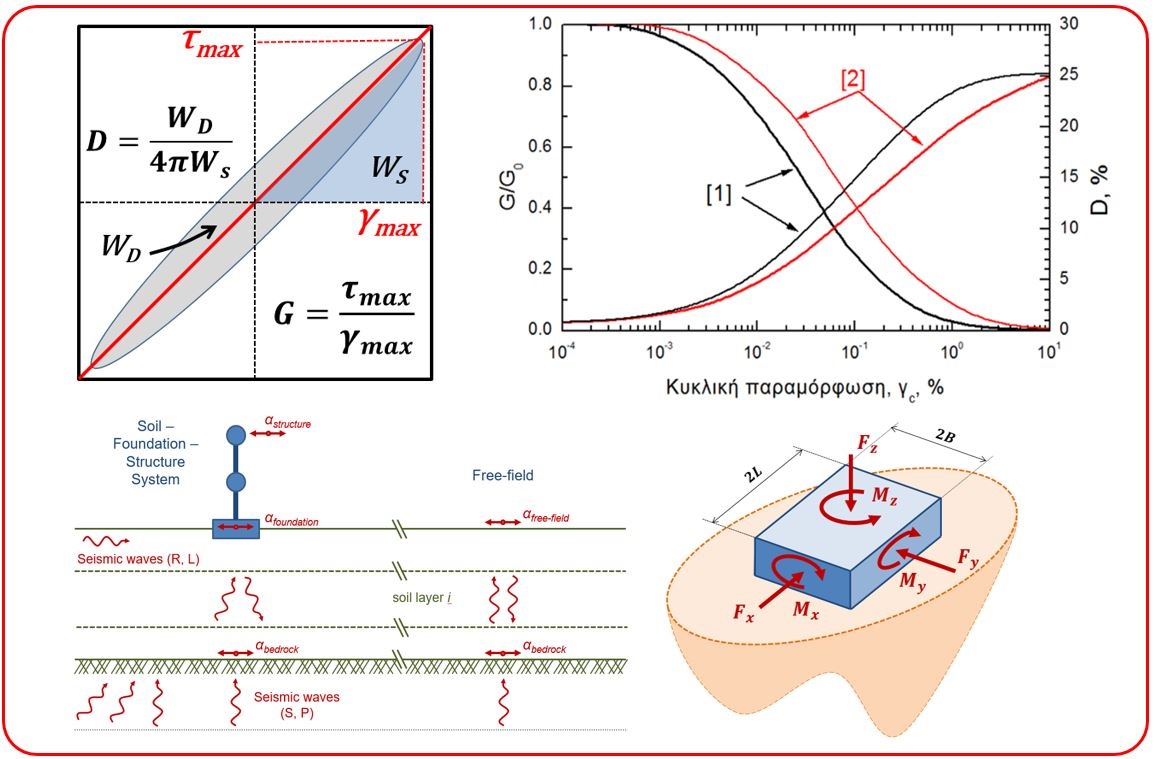
Identification of shear modulus and damping ratio as the most important dynamic soil properties. The effects of: confining stresses, duration of loading, void ratio, amplitude of vibration, number of cycles of loading and loading history on modulus and damping. Analytical models of Hardin-Drnevich and Ramberg-Osgood for describing the stress-strain behavior of soil element.
- VIBRATIONS OF SHALLOW RIGID FOUNDATIONS
Identification of the six degrees of freedom of a rigid foundation. Evaluation of equivalent spring constants, vertical and horizontal vibrations, coupled horizontal and rocking vibrations, torsional vibrations in homogeneous and layered half-space.
- ISOLATION AGAINST GROUND VIBRATIONS
Methods for isolation of man-made ground vibrations. Use of soil trenches, pile-rows and wave impedance (WIB) techniques. Active and passive isolation. Isolation efficiency
- FAILURE CRITERIA
Review of available failure criteria and permissible values of vibration (displacement, velocity, acceleration) for different categories of structures and processes.