1. INTRODUCTION
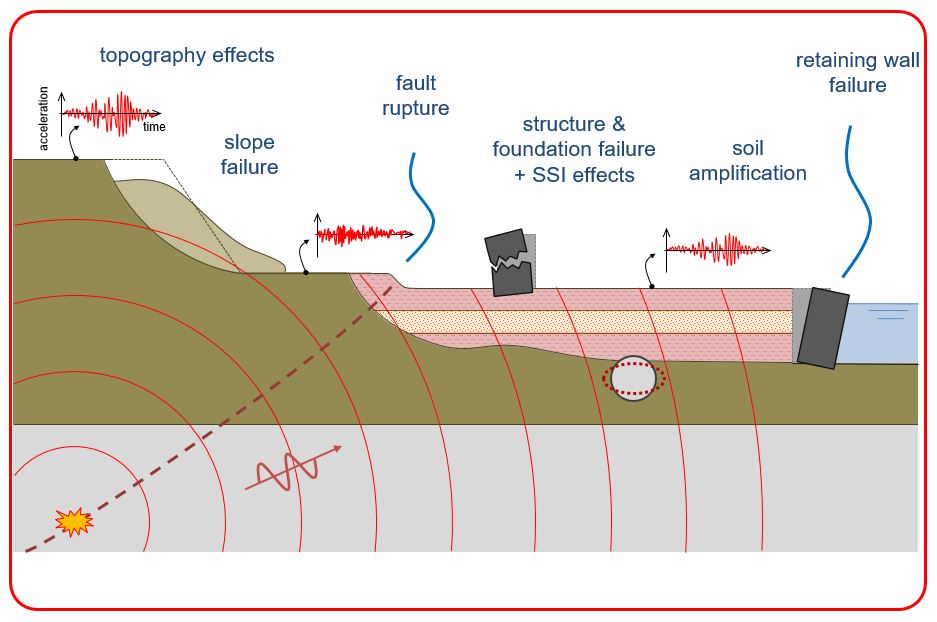
Background, Seismic Hazards (ground shaking, structural hazards, liquefaction, landslides, retaining structures failures, lifeline hazards), mitigation of seismic hazards, significant historical earthquakes.
2. ELEMENTS OF ENGINEERING SEISMOLOGY
Internal structure of the earth, continental drift and plate tectonics, faults, elastic rebound theory, location and magnitude of earthquakes.
3. GROUND RESPONSE ANALYSIS
One-Dimensional ground response analysis (linear approach, nonlinear approach). Two-Dimensional ground response analysis (dynamic Finite Element Analysis, equivalent linear approach. Effect of local soil conditions and topography effects.
4. SOIL LIQUEFACTION
Liquefaction related phenomena (flow liquefaction, cyclic mobility, lateral spreading). Evaluation of liquefaction hazards. Liquefaction susceptibility (historical criteria, geological criteria, state criteria). Liquefaction triggering (flow liquefaction surface, influence of Excess Pore Pressure, evaluation of initiation of liquefaction). Effects of liquefaction (Alteration of ground motion, Development of sand boils, settlement, instability)
5. SEISMIC SLOPE STABILITY
Types of earthquake – induced landslides. Earthquake-induced Landslide activity. Evaluation of slope stability. Static slope stability analysis (limit equilibrium analysis, stress-deformation analyses). Seismic slope stability analysis (analysis of inertial instability, analysis of weakening instability)
6. SEISMIC DESIGN OF RETAINING STRUCTURES
Types of retaining walls. Types of retaining wall failures. Static pressures on retaining walls. Dynamic response of retaining walls. Seismic pressures on retaining walls. Seismic displacements of retaining walls. Seismic Design considerations.
7. SEISMIC CODES & MICROZONATION STUDIES
Modern Geotechnical Seismic Design
| Code | GPOL_A_16016 |
|---|---|
| Instructor | KONTOE STAVROYLA |
| eclass | https://eclass.upatras.gr/courses/CIV1775/ |
| Mandatory/Optional | Elective |
| Credits ECTS | 7,5 |
| ΠΕΡΙΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΟΣ |
At the end of this course the students will be able to:
1. Identify the Seismic Hazard in terms of ground shaking, structural hazards, liquefaction, landslides, retaining structures and lifeline hazards.
2. Understand the sources of seismic activity and ground motions parameters.
3. Use analytical and numerical models to predict the ground motion taking under consideration the effect of local site conditions and topography effects.
4. Estimate the risk against soil liquefaction.
5. Analyse and calculate the dynamic response of ground slopes and retaining structures.
6. Understand the principals and usage of seismic codes and microzonation studies.